Gateway Models
Synopsis
The Dynamic Simulation Environment (DSE) provides a Gateway API which can be used to connect remote simulations, via a gateway model, to a running DSE simulation. A gateway model takes care of signal exchange and time synchronisation between the remote simulation and the DSE simulation. Signals can be either scalar values or binary strings, the latter enabling virtual bus connections between simulation environments.
The gateway model runs in the remote simulation, and is written in that systems native language (or modelling construct). Connections from the gateway model to the DSE simulation are implemented with platform independent protocols, the resultant distributed simulation may combine any number of operating systems and processor architectures.
#include <dse/modelc/gateway.h>
/* Setup the gateway. */
ModelGatewayDesc gw;
model_gw_setup(&gw, "gateway", yaml_files, LOG_INFO, step_size, end_time);
/* Run the simulation. */
while (model_time <= end_time) {
marshal_signal_vectors_out(gw->sv);
int rc = model_gw_sync(&gw, model_time);
marshal_signal_vectors_in(gw->sv);
...
}
/* Exit the simulation. */
model_gw_exit(&gw);
Design
Deployment
A generalised deployment showing how a remote simulation is connected to a DSE simulation using a gateway model. Each simulation has several models, synchronisation and signal exchange are achieved via the gateway model.
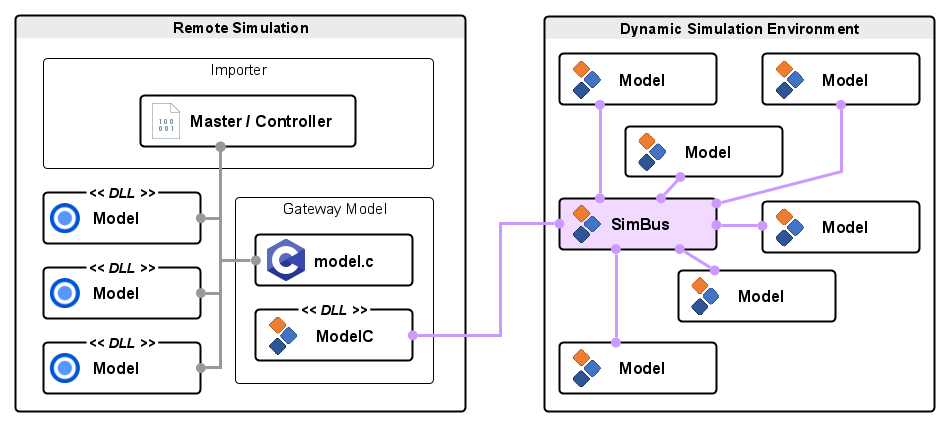
Gateway Model Deployment
Sequence Diagram
The following diagram shows how a gateway model running in a remote simulation interacts with a DSE simulation.
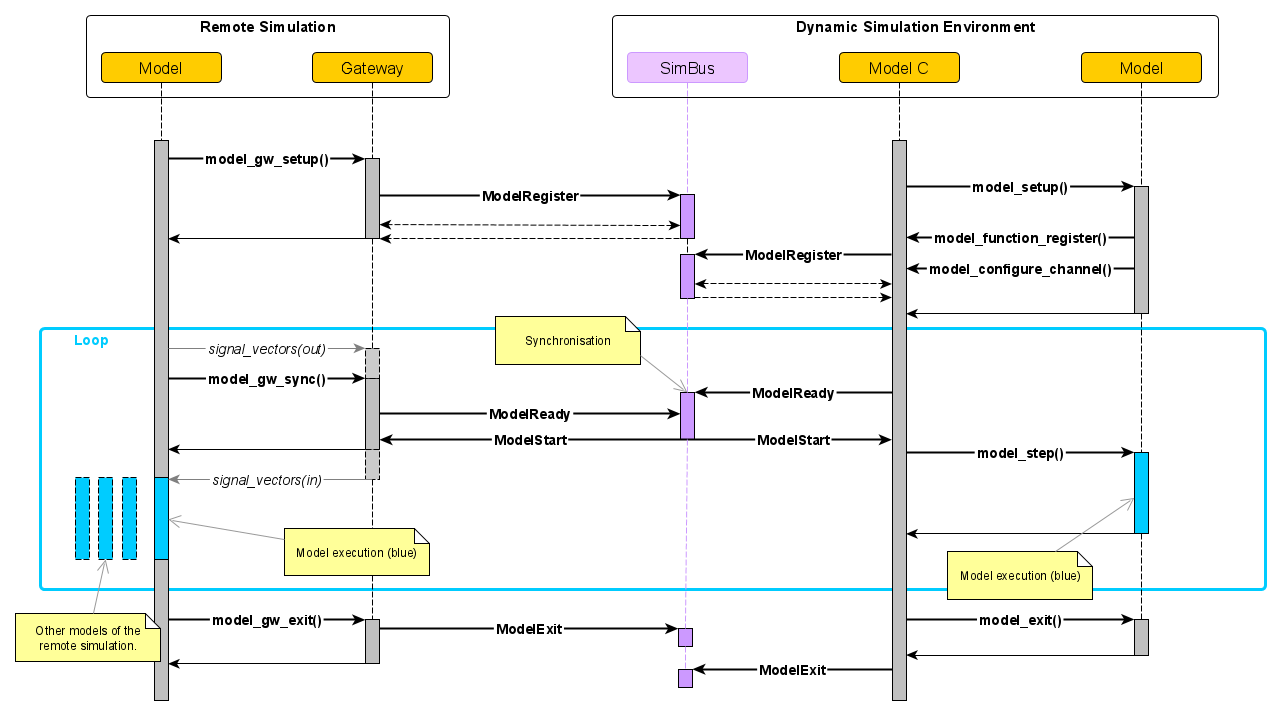
Gateway Model Sequence Diagram
References
- dse/modelc/gateway.h - Gateway API header file.
- dse/modelc/model/gateway.c - Gateway API implementation and documentation.
- dse/modelc/examples/gateway - Example gateway model.